KUUZA VITABU

Hii ni sehemu ya Kitini (Nukuu Fupi) cha Physics Forms 1, 2, 3 & 4 kilicho pewa jina la "Understand O-level Physics Concepts".
Ukihitaji Nakala yote wasiliana nasi kwa namba za simu au email iliyo wekwa ndani ya website hii.
TOPICS TO BE COVERED:
- Static Electricity
- Current Electricity
- Magnetism
- Forces in equilibrium
- Simple machine
- Motion in a straight line
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Temperature
- Sustainable energy sources
TOPIC 01: STATIC ELECTRICITY
Static Electricity is the study of
charge at rest. Static electricity also called electrostatics
Charge
Defn: charge is the particles carry either positive particle or negative particle
Origin of Charges
When body rubbed cause the atoms to loose or gain electron which are revolve around atomic structure result causing the body to become charged. Due to that reason it tends to cause;
(a)plastic materials are rubbed on a
cloth/hair attract dust and small pieces of paper
(b)Particles of wheat are attracted to amber.
(c)The moving parts of machinery, car tyres, and vehicle bodies they attract light particles
(d)Ebonite rubbed with fur/cloth attract dust and small pieces of paper
(e)Glass rubbed with silk attract dust and small pieces of paper
(f) polythene rubbed with fur/cloth attract dust and small pieces of paper
(g)polystyrene rubbed with fur/cloth attract dust and small pieces of paper
(h) Perspex rubbed with woolen cloth attract dust and small pieces of paper
(i) cellulose rubbed with woolen cloth attract dust and small pieces of paper
(j) some clothes cling to the body
(k) comb rubbed with sleeve attract piece
of paper
(l) crackling noise while remove nylon cloth
Types of Electric Charges
There are two types of charge include
i. Positive charge (+)
ii. Negative charge (-)
Positive charge
Defn: Positive charge is a charge acquire when an object loose electron from its atomic structure.
Negative charge
Defn: Negative charge is a charge acquire when an object gain electron from its atomic structure.
Nb:
i. Electrons are revolve around the nuclear.
ii. Electrons are moved from one atom to another.
iii. Protons never move from one to another atom.
Charge acquired after rubbed
Materials | Rubbed with | Charge |
Ebonite | Fur/cloth | Negative |
Glass | Silk | Positive |
Polythene | Cloth/fur | Negative |
Polystyrene | Cloth/fur | Negative |
Perspex | Woolen cloth | Positive |
cellulose | Woolen cloth | Positive |
Fundamental law of electrostatics
The fundamental law of electrostatics which states that
“Like charges repel, unlike charges attract
each other”
Also is called fundamental law of static charges or first law of electrostatics
Charging
Defn: charging is the process whereby material loose or gain electrons
Methods of Charging
There are three methods as
i. Rubbing or friction method
ii. Conduction or contact method
iii. induction method
Friction Method
When you rub two objects the one which his outer most shell weak bound will lose and the one have sparsely electron gain the electron. Due to that electrons shift
from one object to another and tend to gin one to become negative charged and lose one become positive charged
Contact Method
When charge and uncharged body contact the charge always move from charged body to another because like charge repel and unlike charge attract.
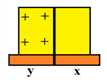
Consider the two charge body (y) and uncharged body (x)
 Contact two bodies.
Contact two bodies.
Since like charge repel each other positive charge will shift/migrate from y to x
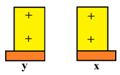
 Separate them immediately
Separate them immediately
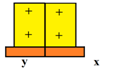
Now uncharged (x) became positive charged



